栈就像是被堆起来的书,最后被堆进去的书在最上边,所以栈有后进先出的特点(last In First Out-FILO)。栈的实现可以使用数组,也可以使用单链表。
Python实现栈(使用列表)
#栈的基本实现:将list包装成类,然后给一些方法
class stack(object):
#初始化栈为空列表
#如果要定义栈中只有items成员,可以 __slot__=('__items')
def __init__(self):
self.items = [] #self.__items私有属性
#判断栈是否为空,返回布尔值
def is_empty(self):
return self.items == []
#返回栈的大小
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
#返回栈顶元素(实际上就是返回列表的最后一个元素)
def peek(self):
return self.items[self.size() - 1]
#压栈,入栈,进栈(把元素放在列表尾部)
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
#出栈(把栈顶的元素丢出去)
def pop(self):
self.items.pop() #pop()函数是移除列表末尾的元素
if __name__ == '__main__':
#实例化
my_stack = stack()
#把Hello丢进栈
my_stack.push('H')
my_stack.push('e')
my_stack.push('l')
my_stack.push('l')
my_stack.push('o')
#查看栈的大小
print(my_stack.size())
#查看栈顶的内容
print(my_stack.peek())
#把栈顶元素丢出去
my_stack.pop()
my_stack.pop()
my_stack.pop()
#查看栈顶元素
print(my_stack.peek())
#查看栈的大小
print(my_stack.size())
#查看栈是否为空
print(my_stack.is_empty())
print("over")
C语言实现栈
使用一维数组实现顺序栈
#include <math.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int Position;
typedef struct SNode *PtrToSNode;
struct SNode {
int *Data;
Position Top;
int MaxSize;
};
typedef PtrToSNode Stack;
Stack Creat_stack(int MaxSize) {
Stack S = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
S->Data = (int *)malloc(MaxSize * sizeof(int));
S->Top = -1;
S->MaxSize = MaxSize;
return S;
}
// if full
bool Isfull(Stack S) {
return ((S->Top) == (S->MaxSize - 1));
}
// push
bool Push(Stack S, int X) {
if (Isfull(S)) {
printf("The Stack is full!");
return false;
}
else {
S->Data[++(S->Top)] = X;
return true;
}
}
// is empty
bool Isempty(Stack S) {
return ((S->Top) == -1);
}
// Pop
int Pop(Stack S) {
if (Isempty(S)) {
printf("The Stack is empty!");
return 114514;
}
else {
return (S->Data[(S->Top)--]);
}
}
int GetTop(Stack S) {
if (Isempty(S)) return 114514;
return S->Data[S->Top];
}
int main() {
Stack my;
int a = 0;
my = Creat_stack(5);
Push(my, 10);
Push(my, 15);
printf("%d\n", GetTop(my));
Pop(my);
printf("%d\n", GetTop(my));
}
使用单链表实现栈
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define ERROR 114514
typedef struct SNode *PtrToSNode;
typedef int ElementType;
struct SNode {
ElementType Data;
PtrToSNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToSNode Stack;
Stack CreatStack() {
/*构建一个堆栈的头结点,返回该节点的指针*/
Stack S;
S = malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
S->Next = NULL;
return S;
}
bool Isempty(Stack S) {
return (S->Next == NULL);
}
bool Push(Stack S, ElementType X) {
/*将元素压入堆栈*/
PtrToSNode TmpCell;
TmpCell = (PtrToSNode)malloc(sizeof(struct SNode));
TmpCell->Data = X;
TmpCell->Next = S->Next;
S->Next = TmpCell;
return true;
}
ElementType Pop(Stack S) {
PtrToSNode FirstCell;
ElementType TopEle;
if (Isempty(S)) {
printf("这是一个空栈");
return ERROR;
}
else {
FirstCell = S->Next;
TopEle = FirstCell->Data;
S->Next = FirstCell->Next;
free(FirstCell);
return TopEle;
}
}
ElementType GetTop(Stack S) {
if (Isempty(S)) {
printf("这是一个空栈\n");
return ERROR;
}
else {
return S->Next->Data;
}
}
int main() {
Stack S;
ElementType top = 0;
ElementType kick = 0;
S = CreatStack();
Push(S, 10);
Push(S, 15);
Push(S, 1);
top = GetTop(S);
printf("%d\n", top);
kick = Pop(S);
printf("%d\n", kick);
kick = Pop(S);
printf("%d\n", kick);
kick = Pop(S);
printf("%d\n", kick);
kick = Pop(S);
printf("%d\n", kick);
return 0;
}
程序运行结果为:
1
1
15
10
这是一个空栈114514
关于含有头结点的链栈的一些解释
下图可以看出数据Data入栈的过程(个人理解,如有错误敬请指出)
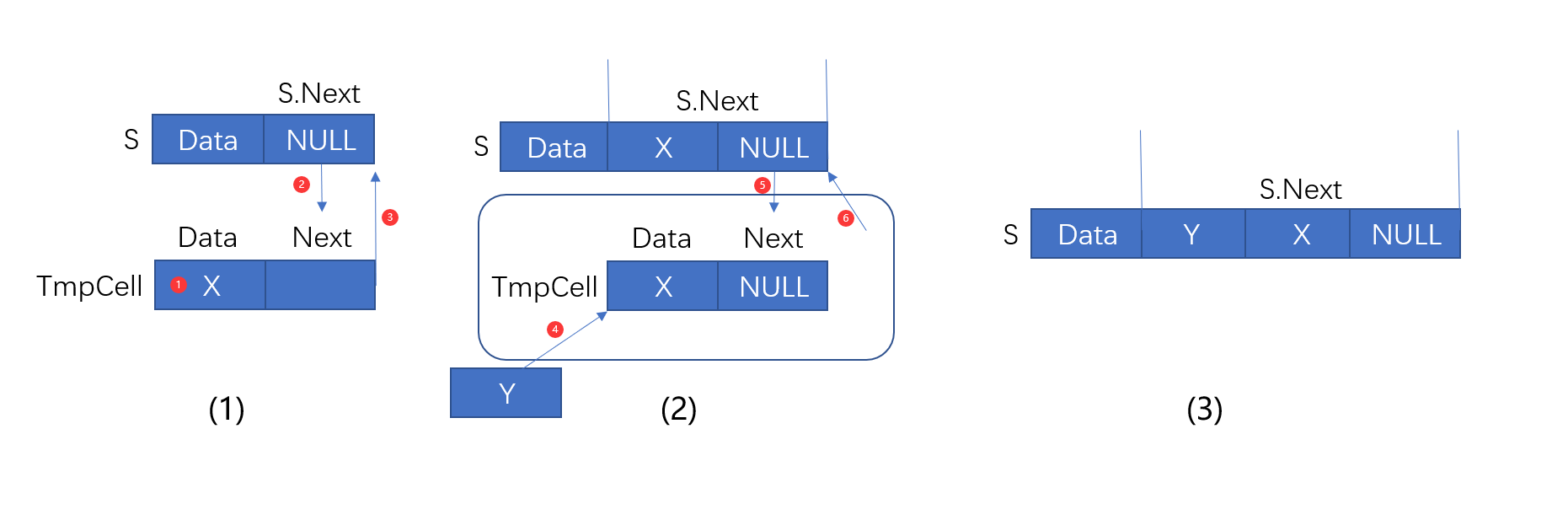 当将10和15依次压入堆栈的时候可以看出来
当将10和15依次压入堆栈的时候可以看出来S的结构如下:
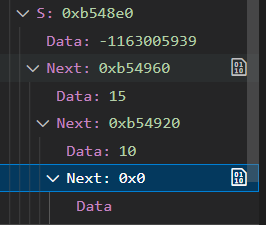 可以看出
可以看出next本身也是一个struct的数据类型,含有Data和Next两个元素,所以可以无限嵌套形成单链表。