1. 网络的初始化
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, sizes):
"""
sizes : 神经元的层数和数量, [2, 3, 1] 三层, 第一层2个神经元, 第二层3个神经元, 第三层1个神经元
"""
self.num_layers = len(sizes) # 神经元层数
self.sizes = sizes
self.biases = [np.random.randn(y, 1) for y in sizes[1:]] # 初始化偏置
self.weights = [
np.random.randn(y, x) for x, y in zip(sizes[:-1], sizes[1:])
] # 初始化权重
假如初始化 net = Network([2,3,1])
- 神经网络初始化需要的参数sizes,是一个包含各层神经元数量的列表,如
sizes = [2,3,1]即表示一个三层的神经网络,第一层有两个神经元,第二层有三个神经元,最后一层含有一个神经元。 self.biases = [np.random.randn(y, 1) for y in sizes[1:]]随机初始化偏置,生成一个包含每层偏置的向量的列表,大小为[(3,1),(1,1)]。后一层有几个神经元就有几个偏置。self.weights = [ np.random.randn(y, x) for x, y in zip(sizes[:-1],sizes[1:])]随机初始化权重,生成一个包含每层权重的向量的列表,大小为[(3,2),(1,3)]。每层之间有多少连线就有多少个权重。
综上,偏置和权重的数量取决于神经元的数量,如果第一层有n个神经元,第二层有m个神经元,则第一层和第二层的连接有m个偏置,有m×n个权重,如下图所示。
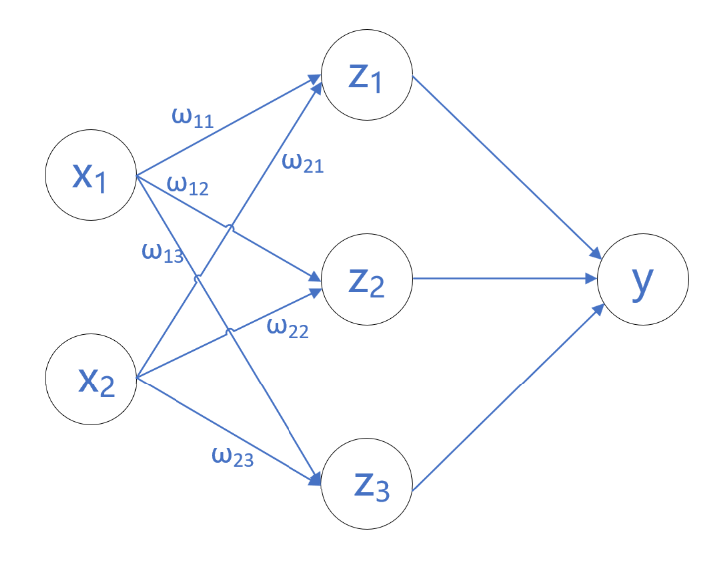 表达式为:
\(\left\{ \begin{align} z_{1} &= w_{11}x_{1}+w_{21}x_{2}+b_{1} \\ z_{2} &=w_{12}x_{1}+w_{22}x_{2}+b_{2} \\ z_{3} &= w_{13}x_{1}+w_{23}x_{2}+b_{3}\end{align} \right.\)
用向量表达为:
\(Z=W X ^ + B\)
表达式为:
\(\left\{ \begin{align} z_{1} &= w_{11}x_{1}+w_{21}x_{2}+b_{1} \\ z_{2} &=w_{12}x_{1}+w_{22}x_{2}+b_{2} \\ z_{3} &= w_{13}x_{1}+w_{23}x_{2}+b_{3}\end{align} \right.\)
用向量表达为:
\(Z=W X ^ + B\)
2. 前向传播
def feedforward(self, a):
"""
实现前向传播
Args:
a 输入向量
"""
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
a = sigmoid(np.dot(w, a) + b)
return a
前向传播的函数表达式为: \(a=\sigma(z)\) 其中: \(z=\omega \times x +b\) 激活函数sigmoid函数: \(\sigma(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-1}}\)
3. 随机梯度下降
def SGD(self, training_data, epochs, mini_batch_size, eta, test_data=None):
"""使用小批量随机梯度下降算法训练神经网络
Args:
training_data : 训练数据
epochs : 训练轮数
mini_batch : 一个batch的大小
eta : learning rate 学习率
test_data : 测试数据, 默认为None
"""
if test_data:
n_test = len(test_data)
n = len(training_data)
for j in range(epochs):
random.shuffle(training_data) # 随机打乱
mini_batchs = [
training_data[k : k + mini_batch_size]
for k in range(0, n, mini_batch_size)
] # 生成训练用的batchs
for mini_batch in mini_batchs:
self.update_mini_batch(mini_batch, eta) # 更新batch
# 打印当前批次信息
if test_data:
print("Epoch{0}:{1}/{2}".format(j, self.evaluate(test_data), n_test))
else:
print("Epoch{} complete".format(j))
SGD:Stochastic Gradient Descent 随机梯度下降
4. 反向传播
import random
import numpy as np
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, sizes):
"""
sizes : 神经元的层数和数量, [2, 3, 1] 三层, 第一层2个神经元, 第二层3个神经元, 第三层1个神经元
"""
self.num_layers = len(sizes) # 神经元层数
self.sizes = sizes
self.biases = [np.random.randn(y, 1) for y in sizes[1:]] # 初始化偏置
self.weights = [
np.random.randn(y, x) for x, y in zip(sizes[:-1], sizes[1:])
] # 初始化权重
def feedforward(self, a):
"""
实现前向传播
Args:
a 输入向量
"""
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
a = sigmoid(np.dot(w, a) + b)
return a
def SGD(self, training_data, epochs, mini_batch_size, eta, test_data=None):
"""使用小批量随机梯度下降算法训练神经网络
Args:
training_data : 训练数据
epochs : 训练轮数
mini_batch : 一个batch的大小
eta : learning rate 学习率
test_data : 测试数据, 默认为None
"""
if test_data:
n_test = len(test_data)
n = len(training_data)
for j in range(epochs):
random.shuffle(training_data) # 随机打乱
mini_batchs = [
training_data[k : k + mini_batch_size]
for k in range(0, n, mini_batch_size)
] # 生成训练用的batchs
for mini_batch in mini_batchs:
self.update_mini_batch(mini_batch, eta) # 更新batch
# 打印当前批次信息
if test_data:
print("Epoch{0}:{1}/{2}".format(j, self.evaluate(test_data), n_test))
else:
print("Epoch{} complete".format(j))
def update_mini_batch(self, mini_batch, eta):
"""更新神经网络的偏置和权重
Args:
mini_batch : 小批数据
eta : learning rate 学习率
"""
nable_b = [np.zeros(b.shape) for b in self.biases]
nable_w = [np.zeros(w.shape) for w in self.weights]
for x, y in mini_batch:
delta_nable_b, delta_nable_w = self.backprop(x, y)
nable_b = [nb + dnb for nb, dnb in zip(nable_b, delta_nable_b)]
nable_w = [nw + dnw for nw, dnw in zip(nable_w, delta_nable_w)]
self.weights = [
w - (eta / len(mini_batch)) * nw for w, nw in zip(self.weights, nable_w)
]
self.biases = [
b - (eta / len(mini_batch)) * nb for b, nb in zip(self.biases, nable_b)
]
def backprop(self, x, y):
"""反向传播函数
Args:
x (_type_): _description_
y (_type_): _description_
"""
nable_b = [np.zeros(b.shape) for b in self.biases]
nabel_w = [np.zeros(w.shape) for w in self.weights]
# 前馈
activation = x
activations = [x]
zs = []
for b, w in zip(self.biases, self.weights):
z = np.dot(w, activation) + b
zs.append(z)
activation = sigmoid(z)
activations.append(activation)
# 反向传播
delta = self.cost_derivative(activation[-1], y) * sigmoid_prime(zs[-1])
nable_b[-1] = delta
nabel_w[-1] = np.dot(delta, activations[-2].transpose())
for l in range(2, self.num_layers):
z = zs[-l]
sp = sigmoid_prime(z)
delta = np.dot(self.weights[-l + 1].transpose(), delta) * sp
nable_b[-l] = delta
nabel_w[-l] = np.dot(delta, activations[-l - 1].transpose())
return (nable_b, nabel_w)
def evaluate(self, test_data):
"""验证函数
Args:
test_data : 验证集
"""
test_results = [(np.argmax(self.feedforward(x)), y) for (x, y) in test_data]
return sum(int(x == y) for (x, y) in test_results)
def cost_derivative(self, output_activations, y):
"""计算激活值的偏导数"""
return output_activations - y
def sigmoid(z):
"""sigmoid函数"""
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z))
def sigmoid_prime(z):
"""sigmoid函数的导数"""
return sigmoid(z) * (1 - sigmoid(z))